day1
01-求两数之和,给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
//普通做法
// for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// for(int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
// if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
// return new int[]{i, j};
// }
// }
// }
// return null;
// 使用hashmap,时间复杂度log(n)
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int temp = target - nums[i];
if(map.get(temp) != null) {
return new int[]{i, map.get(temp)};
} else {
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
}
return null;
}
}
02-字母异位词分组,给你一个字符串数组,请你将 字母异位词 组合在一起。可以按任意顺序返回结果列表。
字母异位词 是由重新排列源单词的所有字母得到的一个新单词
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
// 将字母异位词排序得到key,key相同的放一起
HashMap<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>();
for(String str : strs) {
char[] arr = str.toCharArray(); // 转换为字符数组
Arrays.sort(arr);
String key = new String(arr);
List<String> list = map.getOrDefault(key, new ArrayList<String>());
list.add(str);
map.put(key, list);
}
return new ArrayList<List<String>>(map.values());
}
}
03-最长连续序列,给定一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,找出数字连续的最长序列(不要求序列元素在原数组中连续)的长度。
class Solution {
public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {
// HashSet去重
HashSet<Integer> integers = new HashSet<>();
for(int num : nums) {
integers.add(num);
}
// 从没有num - 1 的 num开始计算
int cnt = 0;
for(Integer integer : integers) {
if (!integers.contains(integer - 1)) {
int currentCnt = 1;
int currentNum = integer;
while(integers.contains(currentNum + 1)) {
currentCnt += 1;
currentNum += 1;
}
cnt = Math.max(cnt, currentCnt);
}
}
return cnt;
}
}
04-移动零,给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
请注意 ,必须在不复制数组的情况下原地对数组进行操作。
class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
while(right < nums.length) {
if(nums[right] != 0) {
int temp = nums[left];
nums[left] = nums[right];
nums[right] = temp;
left++;
}
right++;
}
}
}
05-盛水最多的容器,给定一个长度为 n 的整数数组 height 。有 n 条垂线,第 i 条线的两个端点是 (i, 0) 和 (i, height[i]) ,找出其中的两条线,使得它们与 x 轴共同构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
//使用双指针
int l = 0;
int r = height.length - 1;
int maxValue = 0;
while(r > l) {
int temp = (r - l) * Math.min(height[l], height[r]);
maxValue = Math.max(temp, maxValue);
if(height[r] < height[l]) {
r--;
} else {
l++;
}
}
return maxValue;
}
}
day2
06-三数之和,给你一个整数数组 nums ,判断是否存在三元组 [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] 满足 i != j、i != k 且 j != k ,同时还满足 nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0 。请你返回所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
// 排序
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) {// 去重
continue;
}
int target = -nums[i];
int k = nums.length - 1;
for(int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
// 去重
if(j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j-1]) {
continue;
}
while(j < k && nums[j] + nums[k] > target) {
k--;
}
// j k 重复不满足
if(j == k) {
break;
}
if(nums[j] + nums[k] == target) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(nums[i]);
list.add(nums[j]);
list.add(nums[k]);
res.add(list);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
07-接雨水,给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
}
}
day3
08-无重复字符的最长字串,给定一个字符串 s ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长 子串 的长度。==滑动窗口==
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
Set<Character> set = new HashSet<>();
int cnt = 0;
char[] cc = s.toCharArray();
for(int l = 0, r = 0; r < s.length(); r++) {
while(r < s.length() && set.contains(cc[r])) {
set.remove(cc[l]);
l++;
}
set.add(cc[r]);
cnt = Math.max(cnt, r - l + 1);
}
return cnt;
}
}
day4
09-找到字符串中所有字母异位词,给定两个字符串 s 和 p,找到 s 中所有 p 的 异位词 的子串,返回这些子串的起始索引。不考虑答案输出的顺序。
异位词 指由相同字母重排列形成的字符串(包括相同的字符串)。==滑动窗口==
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {
int slen = s.length();
int plen = p.length();
if(slen < plen) {
return new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 初始化滑动窗口以及记录p对应的字符串
int[] a = new int[26];
int[] b = new int[26];
for(int i = 0; i < plen; i++) {
++a[s.charAt(i) - 'a'];
++b[p.charAt(i) - 'a'];
}
if(Arrays.equals(a, b)) {
list.add(0);
}
for(int i = 0; i < slen - plen; i++) {
--a[s.charAt(i) - 'a'];
++a[s.charAt(i + plen) - 'a'];
if(Arrays.equals(a, b)) {
list.add(i + 1);
}
}
return list;
}
}
day5
10-和为k的子数组,给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,请你统计并返回 该数组中和为 k 的子数组的个数 。
子数组是数组中元素的连续非空序列.==前缀和==
class Solution {
public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
int cnt = 0, pre = 0;
HashMap<Integer, Integer> mp = new HashMap<>();
mp.put(0, 1);
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
pre += nums[i];
if(mp.containsKey(pre - k)) {
cnt += mp.get(pre - k);
}
mp.put(pre, mp.getOrDefault(pre, 0) + 1);
}
return cnt;
}
}
day6
11-滑动窗口最大值,给你一个整数数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口内的 k 个数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。返回 滑动窗口中的最大值 。
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] res = new int[n - k + 1];
// 创建一个双端队列
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();
// 初始化队列
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
while(!deque.isEmpty()&&nums[i] >= nums[deque.peekLast()]) {
deque.pollLast();
}
deque.offerLast(i);
}
res[0] = nums[deque.peekFirst()];
for(int i = k; i < n; i++) {
while(!deque.isEmpty() && nums[i] >= nums[deque.peekLast()]) {// 始终将窗口的最大值放在队列前面
deque.pollLast();
}
deque.offerLast(i);
while(deque.peekFirst() <= i - k) {// 移除
deque.pollFirst();
}
res[i - k + 1] = nums[deque.peekFirst()];
}
return res;
}
}
day7
12-合并区间,以数组 intervals 表示若干个区间的集合,其中单个区间为 intervals[i] = [starti, endi] 。请你合并所有重叠的区间,并返回 一个不重叠的区间数组,该数组需恰好覆盖输入中的所有区间 。
class Solution {
public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {
Arrays.sort(intervals, new Comparator<int[]>(){
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
return o1[0] - o2[0]; //升序排序
}
});
int[] pre = intervals[0];
int k = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < intervals.length; i++) {
int[] cur = intervals[i];
//当前一个数组和前一个数组比较
if(cur[0] <= pre[1]) {// 左边最大值小于右边最小值
int maxRight = Math.max(cur[1], pre[1]);// 右边界最大值
pre = new int[]{pre[0], maxRight};
} else {// 不包含
intervals[k++] = pre;
pre = cur;
}
}
intervals[k++] = pre;
return Arrays.copyOfRange(intervals, 0, k);// 截断
}
}
13-轮转数组,给定一个整数数组 nums,将数组中的元素向右轮转 k 个位置,其中 k 是非负数。(数组翻转)
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
k %= n;
// 数组翻转
reverse(nums, 0, n - 1);
reverse(nums, 0, k - 1);
reverse(nums, k, n - 1);
}
public void reverse(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
while(start <= end) {
int temp = nums[start];
nums[start] = nums[end];
nums[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
}
14-除自身以外数组的乘积,给你一个整数数组 nums,返回 数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 等于 nums 中除 nums[i] 之外其余各元素的乘积 。题目数据 保证 数组 nums之中任意元素的全部前缀元素和后缀的乘积都在 32 位 整数范围内。请 不要使用除法,且在 O(n) 时间复杂度内完成此题。
class Solution {
public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
// 某个位置的左右数组相乘
int[] left = new int[n];
left[0] = 1;
int[] right = new int[n];
right[n - 1] = 1;
for(int i = 1;i < n; i++) {
left[i] = left[i - 1] * nums[i - 1];
}
for(int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
right[i] = right[i + 1] * nums[i + 1];
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
nums[i] = left[i] * right[i];
}
return nums;
}
}
day8
15-矩阵置零,给定一个 *m* x *n* 的矩阵,如果一个元素为 0 ,则将其所在行和列的所有元素都设为 0 。请使用 原地 算法。
class Solution {
public void setZeroes(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
// 使用标记数组
boolean[] row = new boolean[m];
boolean[] col = new boolean[n];
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(matrix[i][j] == 0) {
row[i] = true;
col[j] = true;
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(row[i] || col[j]) {
matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
}
16-螺旋矩阵,给你一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 matrix ,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。(这道题不难,但需要处理边界,理清楚边界的逻辑)
class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length;
if(m == 0) {
return new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
int n = matrix[0].length;
int startx = 0;
int starty = 0;
int offset = 1;
int count = 1;
int cnt = Math.min(m ,n);
for(int k = 0; k < cnt / 2; k++) {
int i, j;
// 上边界遍历 左闭右开
for(j = starty; j < n - offset; j++) {
list.add(matrix[startx][j]);
}
// 右边界遍历
for(i = startx; i < m - offset; i++) {
list.add(matrix[i][j]);
}
// 下边界遍历
for(j = n - offset; j > starty; j--) {
list.add(matrix[i][j]);
}
// 左边界遍历
for(i = m - offset; i > startx; i--) {
list.add(matrix[i][starty]);
}
// 更新边距距离值
startx++;
starty++;
offset++;
}
// 如果是奇数
if((cnt % 2) == 1) {
if(m > n) {// 剩余中间的那一列
for(int i = startx; i <= m - offset; i++) {
list.add(matrix[i][starty]);
}
} else if(m < n) { // 剩余中间的那一行
for(int j = starty; j <= n - offset; j++) {
list.add(matrix[startx][j]);
}
} else { // 剩余中间的那一个元素
list.add(matrix[startx][starty]);
}
}
return list;
}
}
day9
17-旋转图像, 给定一个 n × n 的二维矩阵 matrix 表示一个图像。请你将图像顺时针旋转 90 度。
你必须在 原地 旋转图像,这意味着你需要直接修改输入的二维矩阵。请不要 使用另一个矩阵来旋转图像。
分两步:先按对角线翻转,再按中间对称轴翻转
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[][] matrix) {
int n = matrix.length;
// 1. 按对角线翻转
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
int temp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i];
matrix[j][i] = temp;
}
}
// 2. 按中间对称轴翻转
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n / 2; j++) {
int temp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[i][n - j - 1];
matrix[i][n - j - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
18-搜索二维矩阵,编写一个高效的算法来搜索 *m* x *n* 矩阵 matrix 中的一个目标值 target 。该矩阵具有以下特性:
- 每行的元素从左到右升序排列。
- 每列的元素从上到下升序排列。
Z形状走法
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
// Z 形状走法
int x = 0;
int y = n - 1;
while(x < m && y >=0) {
if(target == matrix[x][y]) {
return true;
}
if(target > matrix[x][y]) {
x++;
} else {
y--;
}
}
return false;
}
}
day10
19-相交链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Set<ListNode> visited = new HashSet<ListNode>();
ListNode temp = headA;
while(temp != null) {
visited.add(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
temp = headB;
while(temp != null) {
if(visited.contains(temp)) {
return temp;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
return null;
}
}
day11
20-反转链表,给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
保留下一个节点的引用,当前节点下一个节点指向前一个节点,前一个节点向后移,当前节点向后移
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while(curr != null) {
ListNode next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
}
21-回文链表,给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。回文链表:从前往后遍历节点的值和从后往前遍历节点的值一样
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode temp = head;
int[] arr = new int[100000];
int k = 0;
while(temp != null) {
arr[k++] = temp.val;
temp = temp.next;
}
int start = 0;
int end = k - 1;
while(start <= end) {
if(arr[start] != arr[end]) {
return false;
}
start++;
end--;
}
return true;
}
}
22-环形链表,给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
// 龟兔赛跑算法
if(head == null || head.next == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while(slow != fast) {
if(fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return false;
}
// fast 移动 快于 slow
// 如果有回环总会相遇,即slow == fast
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}
}
day12
23-环形链表II,给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) {
return null;
}
HashSet<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
if(set.contains(cur)) {
return cur;
}
set.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
}
24-合并两个有序链表,将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null) {
return list2;
}
if(list2 == null) {
return list1;
}
ListNode a = list1;
ListNode b = list2;
ListNode res = null;
if(a.val > b.val) {
res = b;
b = b.next;
} else {
res = a;
a = a.next;
}
ListNode temp = res;
while(a != null && b != null) {
if(a.val > b.val) {
temp.next = b;
b = b.next;
} else {
temp.next = a;
a = a.next;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
while(a != null) {
temp.next = a;
a = a.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
while(b != null) {
temp.next = b;
b = b.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
return res;
}
}
day13
2024-11-23
25-两数相加,给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
/**
1.相加
2.处理进位
出现的情况:l1长度 >= l2长度 l2长度 > l1长度 末尾进位
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
// 遍历相加
ListNode h1 = l1;
ListNode h2 = l2;
while(h1 != null) {
if(h2 != null) {
h1.val = h1.val + h2.val;
h2 = h2.next;
}
// l2 长度大于 l1长度时
if(h1.next == null && h2 != null) {
h1.next = h2;
break;
}
h1 = h1.next;
}
// 进位
merge(l1);
return l1;
}
public void merge(ListNode head) {
while(head != null) {
if(head.val >= 10) {
head.val = head.val % 10;
// 处理末尾进位
if(head.next == null) {
head.next = new ListNode(0);
}
head.next.val += 1;
}
head = head.next;
}
}
}
day14
26-删除链表的倒数第N个结点,给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ArrayList<ListNode> arr = new ArrayList<>();
if(head == null) {
return null;
}
int len = 0;
ListNode temp = head;
while(temp != null) {
arr.add(temp);
len++;
temp = temp.next;
}
// len -n 移除
if(arr.size() == 1) { // 只有一个元素时
return null;
}
ListNode del = arr.get(len - n);
// 删除的元素为最左边的元素
if(len - n == 0) {
return del.next;
}
ListNode pre = arr.get(len - n - 1);
pre.next = del.next;
return head;
}
}
27-两两交换链表中的节点,给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
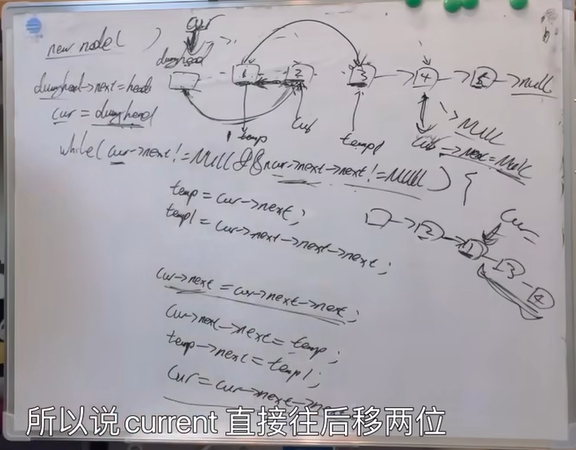
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) {
return null;
}
// 虚拟头结点
ListNode a = new ListNode();
a.next = head;
// 当前结点
ListNode curr = a;
while(curr.next != null && curr.next.next != null) {
ListNode temp1 = curr.next;
ListNode temp2 = curr.next.next.next;
curr.next = curr.next.next;
curr.next.next = temp1;
temp1.next = temp2;
curr = curr.next.next;
}
return a.next;
}
}
day15
28-k个一组翻转链表,给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
// 虚拟头结点
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
// pre节点
ListNode pre = dummy;
// end节点
ListNode end = dummy;
// while循环找到翻转的尾部
while(end.next != null) {
for(int i = 0; i < k && end != null; i++) {
end = end.next;
}
if(end == null) {// 不够k个元素
break;
}
// 记录下一次开始的节点
ListNode next = end.next;
end.next = null;
// 记录当前头结点
ListNode start = pre.next;
pre.next = null;
// 翻转链表
pre.next = reverseList(start);
// 恢复null
start.next = next;
pre = start;
end = start;
}
return dummy.next;
}
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while(curr != null) {
ListNode next = curr.next;
curr.next = pre;
pre = curr;
curr = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
29-随机链表的复制
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
// 采用递归的方式
if(head == null) {
return null;
}
if(!map.containsKey(head)) {
Node newNode = new Node(head.val);
map.put(head, newNode);
newNode.next = copyRandomList(head.next);
newNode.random = copyRandomList(head.random);
}
return map.get(head);
}
}
day16
30-排序链表,给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode curr = head;
int n = 0;// 算出长度
while(curr != null) {
n++;
curr = curr.next;
}
// 存放到数组中
ListNode[] list = new ListNode[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
list[i] = head;
head = head.next;
}
// 排序
Arrays.sort(list, new Comparator<ListNode>(){
@Override
public int compare(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
return l1.val - l2.val; //升序
}
});
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
list[i].next = list[i+1];
}
// 防止循环
list[n-1].next = null;
return list[0];
}
}
31-LRU, 请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity)以 正整数 作为容量capacity初始化 LRU 缓存int get(int key)如果关键字key存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回-1。void put(int key, int value)如果关键字key已经存在,则变更其数据值value;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组key-value。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过capacity,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。
函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
class LRUCache {
// 双向链表
class DlinkedNode{
int key;
int value;
DlinkedNode prev;
DlinkedNode next;
public DlinkedNode() {
}
public DlinkedNode(int _key, int _value) {
key = _key;
value = _value;
}
}
// 哈希表
private Map<Integer, DlinkedNode> cacah = new HashMap<Integer, DlinkedNode>();
private int size;
private int capacity;
// 虚拟头,尾节点
private DlinkedNode head, tail;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.size = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
// 初始化虚拟头,尾节点
head = new DlinkedNode();
tail = new DlinkedNode();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
public int get(int key) {
DlinkedNode node = cacah.get(key);
if(node == null) {
return -1;
}
// 如果key存在,则先通过hash表定位,再移动到头部
moveToHead(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
DlinkedNode node = cacah.get(key);
if(node == null) {
// key不存在,创建一个
DlinkedNode newNode = new DlinkedNode(key, value);
// 添加进hash表
cacah.put(key, newNode);
// 添加到双向链表的头部
addToHead(newNode);
++size;
// 判断size是否大于capacity
if(size > capacity) {
// 超出容量,删除尾部节点
DlinkedNode tail = removeTail();
// 删除hash表中对应的项
cacah.remove(tail.key);
--size;
}
} else {
node.value = value;
// 移动到链表前面
moveToHead(node);
}
}
// 将元素移动到头部
private void moveToHead(DlinkedNode node) {
// 先移除节点
removeNode(node);
// 添加到头部
addToHead(node);
}
// 移除元素
private void removeNode(DlinkedNode node) {
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
// 添加元素到头部
private void addToHead(DlinkedNode node) {
node.prev = head;
node.next = head.next;
head.next.prev = node;
head.next = node;
}
// 删除尾部节点
private DlinkedNode removeTail() {
DlinkedNode res = tail.prev;
removeNode(res);
return res;
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/
32-合并k个升序链表,给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if(lists.length == 0) {
return null;
}
int len = lists.length;
int n = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
ListNode cur = lists[i];
while(cur != null) {
n++;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(n == 0) {
return null;
}
ListNode[] arr = new ListNode[n];
int k = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
ListNode cur = lists[i];
while(cur != null) {
arr[k++] = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(n == 1) {
return arr[0];
}
Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator<ListNode>() {
@Override
public int compare(ListNode n1, ListNode n2) {
return n1.val - n2.val;
}
});
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
arr[i].next = arr[i+1];
}
arr[n-1] = null;
return arr[0];
}
}
day17
33-二叉树的中序遍历,给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回 它的 中序 遍历 。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
inorder(root, res);
return res;
}
public void inorder(TreeNode node, List<Integer> res) {
if(node == null) {
return;
}
// 左 中 右
inorder(node.left, res);
res.add(node.val);
inorder(node.right, res);
}
}
34-二叉树最大深度,二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
} else {
int leftHeight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHeight = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
}
}
35-翻转二叉树,给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
// 后续遍历
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode left = invertTree(root.left);
TreeNode right = invertTree(root.right);
root.left = right;
root.right = left;
return root;
}
}
day18
36-对称二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
// 后续遍历
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return check(root.left, root.right);
}
public boolean check(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p == null && q == null) {
return true;
}
if(p == null || q == null) {
return false;
}
return p.val == q.val && check(p.left, q.right) && check(p.right, q.left);
}
}
37-二叉树的直径,给你一棵二叉树的根节点,返回该树的 直径 。
二叉树的 直径 是指树中任意两个节点之间最长路径的 长度 。这条路径可能经过也可能不经过根节点 root 。
两节点之间路径的 长度 由它们之间边数表示。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
// 对于一个节点,左儿子节点的最大深度为 l 右儿子节点最大深度为 r
// l(左二子节点数) + r(右儿子节点数) + 1(根) = (res)最大路径节点数
// 最大路径长度为 = res - 1
class Solution {
int res;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
res = 0;
dept(root);
return res - 1;
}
public int dept(TreeNode node) {
if(node == null) {
return 0;
}
int l = dept(node.left);
int r = dept(node.right);
// 遍历的节点数量
res = Math.max(res, l + r + 1);
return Math.max(l, r) + 1;
}
}
38-二叉树的层序遍历,给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 层序遍历 。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。==广度优先搜索==
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
// 采用广度优先搜索的方式 + 队列
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if(root == null) {
return res;
}
// 创建一个队列
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int size = queue.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
level.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
res.add(level);
}
return res;
}
}
day19
39-将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树,给你一个整数数组 nums ,其中元素已经按 升序 排列,请你将其转换为一棵 平衡 二叉搜索树。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
// 二叉树的中序遍历刚好是升序数组
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return solve(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode solve(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
if(left > right) {
return null;
}
int mid = (right - left) / 2 + left;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = solve(nums, left, mid - 1);
root.right = solve(nums, mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
}
40-验证二叉搜索树,给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
有效 二叉搜索树定义如下:
-
节点的左
子树
只包含
小于
当前节点的数。
-
节点的右子树只包含 大于 当前节点的数。
-
所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return solve(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE);
}
public boolean solve(TreeNode root, long lower, long upper) {
if(root == null) {
return true;
}
if(root.val <= lower || root.val >= upper) {
return false;
}
return solve(root.left, lower, root.val) && solve(root.right, root.val, upper);
}
}
41-二叉搜索树中的第k小的元素,给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,和一个整数 k ,请你设计一个算法查找其中第 k 小的元素(从 1 开始计数)。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
// 采用中序遍历,遍历得到的顺序就是升序的顺序
class Solution {
public static Integer target = 0;
public static Integer cnt = 0;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
cnt = k;
solve(root);
return target;
}
public void solve(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
solve(root.left);
if(--cnt == 0) {
target = root.val;
}
solve(root.right);
}
}
day20
42-二叉树的右视图,给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
// 采用广度优先搜索方法
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(root == null) {
return res;
}
// 定义双端队列
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(i == size - 1) {
res.add(node.val);
}
if(node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
43-二叉树展开为链表,给你二叉树的根结点 root ,请你将它展开为一个单链表:
展开后的单链表应该同样使用 TreeNode ,其中 right 子指针指向链表中下一个结点,而左子指针始终为 null 。
展开后的单链表应该与二叉树 先序遍历 顺序相同。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
// 主要考察先序遍历
class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
List<TreeNode> list = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
solve(root, list);
int size = list.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
TreeNode temp = list.get(i);
temp.right = list.get(i + 1);
temp.left = null;
}
}
public void solve(TreeNode root, List<TreeNode> list) {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
list.add(root);
solve(root.left, list);
solve(root.right, list);
}
}
44-从前序遍历与中序遍历序列构造二叉树,给定两个整数数组 preorder 和 inorder ,其中 preorder 是二叉树的先序遍历, inorder 是同一棵树的中序遍历,请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return solve(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode solve(int[] preorder, int preStart, int preEnd,
int[] inorder,int inStart, int inEnd) {
// 终止条件
if(preStart > preEnd || inStart > inEnd) {
return null;
}
// 提取根节点
int rootVal = preorder[preStart];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
// 中序遍历中找到根节点的位置
int rootIndex = -1;
for(int i = inStart; i <= inEnd; i++) {
if(rootVal == inorder[i]) {
rootIndex = i;
break;
}
}
// 左子树个数
int leftCnt = rootIndex - inStart;
// 这里的下标需要好好理解
// 构建左子树
root.left = solve(preorder, preStart + 1, preStart + leftCnt,
inorder, inStart, rootIndex - 1);
// 构建右子树
root.right = solve(preorder, preStart + leftCnt + 1, preEnd,
inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd);
return root;
}
}
45-路径总和,给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,和一个整数 targetSum ,求该二叉树里节点值之和等于 targetSum 的 路径 的数目。
路径 不需要从根节点开始,也不需要在叶子节点结束,但是路径方向必须是向下的(只能从父节点到子节点)。
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1UU4y1A7BE/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click&vd_source=32fb884356739c022c7ef3750cdd7abe
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
// 采用回溯法 + 前缀和 + 先序遍历
class Solution {
public HashMap<Long, Integer> prefixSum = new HashMap<Long, Integer>();
public Integer cnt = 0;
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
prefixSum.put(0L, 1);
backTrack(root, 0, targetSum);
return cnt;
}
// 回溯
public void backTrack(TreeNode root, long sum, int targetSum) {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
// 更新当前路径和
sum += root.val;
if(prefixSum.containsKey(sum - targetSum)&&prefixSum.get(sum - targetSum)>=1) {
cnt += prefixSum.get(sum - targetSum);
}
// 记录当前前缀和
prefixSum.put(sum, prefixSum.getOrDefault(sum, 0) + 1);
// 遍历左子树
backTrack(root.left, sum, targetSum);
// 遍历右子树
backTrack(root.right, sum, targetSum);
// 状态回归
prefixSum.put(sum, prefixSum.get(sum) - 1);
}
}
